ENGG 1015 Tutorial Digital Logic (II) (70 pages) 15 Oct Learning Objectives Learn about Boolean Algebra (SoP/PoS, DrMorgan's Theorem, simplification), Karnaugh map, Full adder, Flip. Describe the function using Boolean expressions Draw the truth table and describe the function using sum of product. View Homework Help - HardwareTutorial01.pdf from EEE 120 at Arizona State University. Tutorial 1: Boolean Algebra 1. On my last visit to the National Film theatre I noticed that my ticket had the. E1.2 Digital Electronics I Oct 2007 Boolean Variables • Boolean variables take the value either 0 or 1 only – if a variable doesn't have the value 0, then it must have the value 1. • In Boolean algebra we use for 'and' and + for 'or' S = H •R + F •R • If we could build an electronic circuit which implemented. Intro to Boolean Algebra and Logic Ckts Rev R.doc, Page 6 of 10 A B Y 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 Using basic Boolean operators the logic for the XOR operator is drawn below. A B AB AB AB AB The output is a “1” when A and B are of different values. The output is “0” when A and B are of the same value. It is said the Y equals A. Boolean Algebra Tutorial Freeware IVSwap v.0.1 Beta iVSwap is a simple function which can be used as a library and swaps values between two variables in a mathematical way using a classic Boolean algebra law without the need of a buffer! Whats new Boolean Algebra Tutorial Pdf Free Download this version This version is the first release on. There are also standalone spam-stoppers out there; as it Boolean Algebra Tutorial Pdf Free Download, one of the best weve tried is also free. CHAPTER 3 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic. 3.1 Introduction 121. 3.2 Boolean Algebra 122. 3.2.1 Boolean Expressions 123. Boolean algebra is a branch of mathematics and it can be used to describe the manipulation and processing of. The two-valued Boolean algebra.
Boolean Algebra Simplification Examples
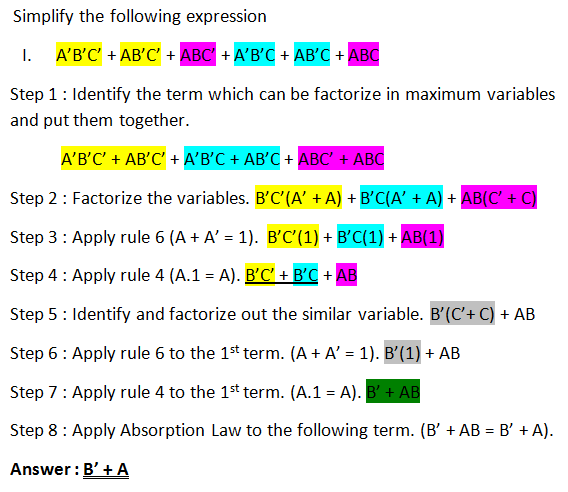
Boolean Algebra Problems And Solutions
Proteus Tutorial for Digital Circuit Design Proteus is one of the most famous simulators. It can be uses to simulate almost every circuit on electrical fields. It is easy to use because of the GUI interface that is very similar to the real Prototype board. Moreover, it can be used to design Print Circuit Board (PCB).
1. Objectives 1. Review students on using proteus software. 2. Introduce how to run simulation of designed digital circuit. 3. Understand how to applied digital logic equation to real hardware designs
2. Tools and equipment specifications Proteus sotware
3. Review topics: 1. Boolean algebra 2. Basic logic operation (for examples, and, or, not, and, etc.)
4. Related Theory Proteus has many features to generate both analogue and digital result. However, this lab will focus on only tools that will be used in digital schematic designs.
Figure 1: Example of Proteus software window.
Proteus that will be used in the lab is version 6.9 with service pack 9 can be called from Start>>Program>>Proteus 6 Professional>>ISIS 6 professional. 1. Proteus tools. a. Parts Browsing Proteus has many models of electronic equipments such as logic gates, many kinds of switches and basic electronic devices. and then . These equipments can be founded by clicking on Then, a new window will pop up and wait for the part’s information as shown in the Figure 2.
Figure 2 : Example of pick device page(1)
Finding Steps: 1. Type information of the device such as “and gate” in the box 1 2. If some specific category is known, the device can narrow on focusing by selecting catalogue in the box 2 3. After the information is put, the list of the related devices will appear in the box 3, so that needed device can be choose here and then click “OK” button to confirm the selection as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Example of picking device page(2) b. Power Supplies and input signal generators All of the electrical circuits require power supplies. The power supply for logic gates are represented in the digital system design on proteus because the schematic will be too complicated to understand for simulation section. Therefore, the power supplies will be need as input power for a system. Moreover, all of the input generators, such as ac, dc, and pulse, are contained in this category and it will be shown are clicked. Inaddition, “Ground” will not contain in this when groups because it is not input signal but it is just a terminal junction. Therefore it will be group in the terminal ( ) category as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 4
Figure 5
In addition, there is another input that usually be used in digital circuit designed system but it does not exist in real world as an equipment. It is called as “LOGIC STATE”. It can be find in picking part section (typing “logicstate” and pick it.
Figure 6: logic state 2. How to do the simulating a. Placing Equipments After selecting all the devices, now devices needed to be placeb on the circuit sheet (Grey sheet) and wiring before the simulation can be run by following these steps: and select a first device that will be placed 1. Click on 2. Place mouse to wherever the device is preferred to be place and then click the left button of the mouse. The device will be place. If it needed to be moved. Click the right button of the mouse on the device symbol to select the part and then hold the left button of the mouse and move the symbol to wherever it is needed to be places.
Figure 7: placing the parts
3. To wire the device together, click at the source pin of the device and then move mouse cursor to the destination pin of the device. In this step the pink line will be appear and it will be the wire of the circuit after click mouse on the destination pin of the circuit (as shown in figure 8)
Figure 8 4. After wiring all of the devices and all input together, the simulation is ready to be run by clicking on to run and to stop. However, to see the result measurements needed to be added in the circuit. They will be explained in next part. b. Measuring Digital data Actually, the digital result on proteus can be seen in small square at the pin of the equipments and the state will be shown in 4 colors (red = logic “1”, Blue = logic ”0”, Grey = Unreadable logic and Yellow = Logic congestion). However, proteus build a modules that can be used to show the logic in 2 ways. 1. Logic display The display that proteus has for seeing logic value is called “logic-probe”. It has 2 sizes and these seizes have the same functions. And it can be found from “picking devices” page
Figure 9 Logic Probe
2. Waveform display. In the low frequency case, logic-probe is the easiest way for digital logic analysis because human eyes can see the result of the simulation. Also, logic-probe also works for high frequency system but human eyes can not see the results. Therefore, proteus create digital logic analyzer for the high frequency jobs. To use the logic analyzer on proteus following these steps. 1. Click on and place the voltage probe to the point the needed to measure. After connect the probe to measured point, the probe will be named as identifier of the measure point. 2. Click on and select “digital” from “Graphs” box then assign the are of digital display. The Green screen will appear as measurement monitor as shown in the figure 10
Figure 10 Example of digital analysis 3. Clicking at the word “DIGITAL ANALYSIS” on the screen. New window will appear as the expanded screen as shown in figure 11.
Figure 11
4. Click on graph>> add trace, new pop up window will appear to add the measure points needed on “Probe P1” (if many probes appear on the design, proteus may ask to offer all probes adding) then click OK. The select probes will be added on the screen.
Figure 12 5. To see the result of the design, for 1 second.
must be clicked to simulation
Figure 13 Example of a digital circuit design
4. Assignments 4.1 Create digital circuit from the equation below and write truth tables a. b. c. 4.2 Compare the result of equation b and c from 4.2. Do they have the same results? If so, show the Boolean algebra analysis to reduce the equation from b to c. Gives the advantage of using Boolean algebra for the circuit design. 4.3 Plot the relationship between all of the inputs and outputs of the circuit diagram below
• •
Input X with 10kHz square wave or clock, Input Y with 20kHz clock, and Input Ci with 30kHz clock. Outputs are S and Co